How to remove a server
In this recipe we'll learn how to work out to remove a server from a Pinot cluster.
Prerequisites
To follow the code examples in this guide, you must install Docker (opens in a new tab) locally and download recipes.
Navigate to recipe
- If you haven't already, download recipes.
- In terminal, go to the recipe by running the following command:
cd pinot-recipes/recipes/removing-serverLaunching Pinot Cluster
Create Kubernetes cluster:
kind create clusterYou can spin up a Pinot Cluster by running the following command:
helm repo add pinot https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/pinot/master/kubernetes/helm
kubectl create ns pinot-quickstart
helm install pinot pinot/pinot \
-n pinot-quickstart \
--set cluster.name=pinot \
--set server.replicaCount=4Port Forward Pinot UI on port 9000
kubectl port-forward service/pinot-controller 9000:9000 -n pinot-quickstarthelm repo add kafka https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm install -n pinot-quickstart kafka kafka/kafka --set replicas=1,zookeeper.image.tag=latestPort forward Kafka on port 9090
kubectl port-forward service/kafka-headless 9092:9092 -n pinot-quickstartAdd following line to /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 kafka-0.kafka-headless.pinot-quickstart.svc.cluster.localNext, we're going to deploy a Kafka pod and connect to it:
kubectl run kafka-client --restart='Never' --image docker.io/bitnami/kafka:3.4.0-debian-11-r22 --namespace pinot-quickstart --command -- sleep infinity
kubectl exec --tty -i kafka-client --namespace pinot-quickstart -- bashWe're going to create the events topic with 5 partitions, by running the following command:
kafka-topics.sh \
--create --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--replication-factor 1 \
--partitions 5 \
--topic eventsGenerating data
This recipe contains a data generator that creates events with a timestamp, count, and UUID. You can generate data by running the following command:
python datagen.py 2>/dev/null | head -n1 | jqOutput is shown below:
{
"ts": 1680171022742,
"uuid": "5328f9b8-83ff-4e4c-8ea1-d09524866841",
"count": 260
}Ingesting data into Kafka
We're going to ingest this data into an Apache Kafka topic using the kcat (opens in a new tab) command line tool.
We'll also use jq to structure the data in the key:payload structure that Kafka expects:
python datagen.py --sleep 0.0001 2>/dev/null |
jq -cr --arg sep ø '[.uuid, tostring] | join($sep)' |
kcat -P -b localhost:9092 -t events -KøAdding Pinot Schema and Table
Now let's create a Pinot Schema and Table.
First, the schema:
{
"schemaName": "events",
"dimensionFieldSpecs": [{"name": "uuid", "dataType": "STRING"}],
"metricFieldSpecs": [{"name": "count", "dataType": "INT"}],
"dateTimeFieldSpecs": [
{
"name": "ts",
"dataType": "TIMESTAMP",
"format": "1:MILLISECONDS:EPOCH",
"granularity": "1:MILLISECONDS"
}
]
}schema.json
Now for the table config:
{
"tableName": "events",
"tableType": "REALTIME",
"segmentsConfig": {
"timeColumnName": "ts",
"timeType": "DAYS",
"retentionTimeUnit": "DAYS",
"retentionTimeValue": "3650",
"segmentPushType": "APPEND",
"segmentAssignmentStrategy": "BalanceNumSegmentAssignmentStrategy",
"schemaName": "events",
"replication": "2",
"replicasPerPartition": "2"
},
"tenants": {},
"ingestionConfig":{
"transformConfigs": [
{
"columnName": "ts",
"transformFunction": "FromDateTime(tsString, 'YYYY-MM-dd''T''HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS''Z''')"
}
]
},
"tableIndexConfig": {
"loadMode": "MMAP",
"streamConfigs": {
"streamType": "kafka",
"stream.kafka.consumer.type": "simple",
"stream.kafka.topic.name": "events",
"stream.kafka.decoder.class.name": "org.apache.pinot.plugin.stream.kafka.KafkaJSONMessageDecoder",
"stream.kafka.consumer.factory.class.name": "org.apache.pinot.plugin.stream.kafka20.KafkaConsumerFactory",
"stream.kafka.hlc.zk.connect.string": "kafka-zookeeper:2181",
"stream.kafka.zk.broker.url": "kafka-zookeeper:2181",
"stream.kafka.broker.list": "kafka:9092",
"realtime.segment.flush.threshold.time": "3600000",
"realtime.segment.flush.threshold.size": "50000",
"stream.kafka.consumer.prop.auto.offset.reset": "smallest"
}
},
"metadata": {
"customConfigs": {}
}
}table.json
kubectl apply -f config/pinot-events.ymlChecking segment assignment
As soon as this config has been applied, Pinot will start ingesting the data from Kafka. We'll let it run for a little while and then run the following script to check segment assignment:
python segments_to_server.py \
--segments-to-servers false \
--partitions-to-servers false \
--servers-to-partitions trueOutput
Server_pinot-server-0 OrderedSet(['1', '3'])
Server_pinot-server-1 OrderedSet(['0', '2', '4'])
Server_pinot-server-2 OrderedSet(['0', '2', '4'])
Server_pinot-server-3 OrderedSet(['1', '3'])We can see that the partitions are spread across servers 0-3.
Removing server from cluster
Next, we're going to remove a server from the Pinot cluster:
kubectl scale statefulset.apps/pinot-server -n pinot-quickstart --replicas=3After we've done this, be should see one 'dead' server on the Pinot UI:
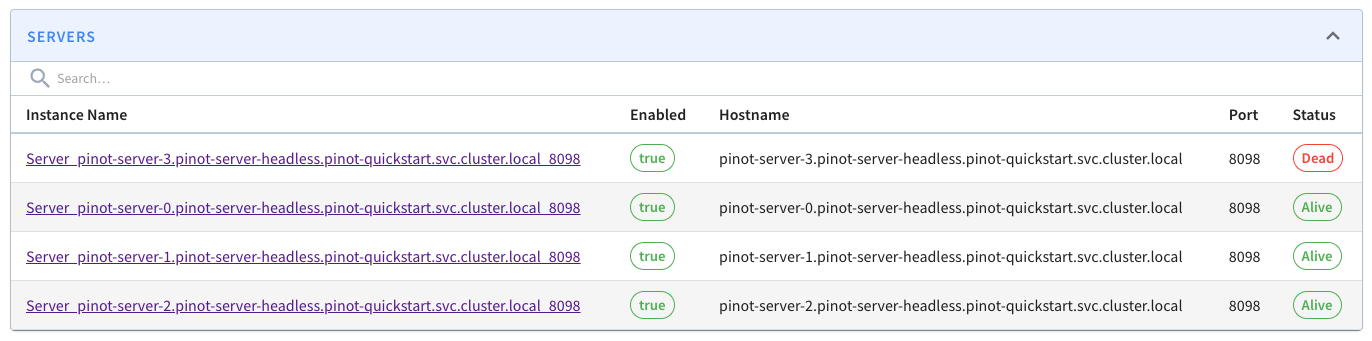 List of Pinot servers with one dead
List of Pinot servers with one dead
In this example server 3 has been removed, but your mileage may vary.
So, the underlying server has been removed, but Pinot still thinks its there. Pinot has an API that lets us remove instances, so let's try that out:
Try to remove the instance:
instance="Server_pinot-server-3.pinot-server-headless.pinot-quickstart.svc.cluster.local_8098"
curl -X DELETE \
"http://localhost:9000/instances/${instance}" \
-H "accept: application/json"It didn't work because the server is still part of the ideal state for the table.
Removing tags from server
To fix this, we need to first remove all the tags from that server, by running the following:
instance="Server_pinot-server-3.pinot-server-headless.pinot-quickstart.svc.cluster.local_8098"
curl -X PUT \
"http://localhost:9000/instances/${instance}/updateTags?tags=&updateBrokerResource=false" \
-H "accept: application/json"Output
{
"status":"Updated tags: [] for instance: Server_pinot-server-3.pinot-server-headless.pinot-quickstart.svc.cluster.local_8098"
}This will prevent any new segments being assigned to this server, but we still have one more step to do.
Rebalancing segments
The next is to rebalanae the segments so that any assigned to server 3 will be moved elsewhere.
The API that does this takes in a lot of parameters, so we've wrapped it in the rebalance.py script, which you can download from GitHub.
The contents are shown below:
import requests
import click
import json
@click.command()
@click.option('--table_name', default="events", help='Table name')
def run_rebalance(table_name):
base_url = f"http://localhost:9000/tables/{table_name}/rebalance"
params = {
'type': 'realtime',
'dryRun': 'false',
'reassignInstances': 'true',
'includeConsuming': 'false',
'bootstrap': 'false',
'downtime': 'false',
'minAvailableReplicas': '1',
'bestEfforts': 'false',
'externalViewCheckIntervalInMs': '1000',
'externalViewStabilizationTimeoutInMs': '3600000',
'updateTargetTier': 'false',
}
response = requests.post(base_url, params=params)
print(response.url)
print(response.status_code)
print(json.dumps(response.json(), indent=4))
if __name__ == '__main__':
run_rebalance()rebalance.py
Adjust those parameters accordingly before you run the script. You can run the script like this:
python rebalance.pyIf you then wait a few seconds or maybe longer depending on how many segments you have, the segments will be rebalanced. At the time we're writing this guide there isn't an API to check on the progress of rebalancing, but this will be added in Pinot 0.13.
You can manually check if it's completed by running the following script again:
python segments_to_server.py \
--segments-to-servers false \
--partitions-to-servers false \
--servers-to-partitions trueOnce rebalancing has completed, you shouldn't see server 3 in the output:
Output
Server_pinot-server-0 OrderedSet(['1', '2', '4'])
Server_pinot-server-1 OrderedSet(['0', '1', '3', '4'])
Server_pinot-server-2 OrderedSet(['0', '2', '3'])Removing instance from Pinot
And once that's the case, we can retry the API that removes the instance from Pinot:
instance="Server_pinot-server-3.pinot-server-headless.pinot-quickstart.svc.cluster.local_8098"
curl -X DELETE \
"http://localhost:9000/instances/${instance}" \
-H "accept: application/json"Output
{
"status":"Successfully dropped instance"
}