Ingest from a streaming data source
In this guide you will learn how to import data from a streaming data set. You should have a local cluster up and running, following the instructions in Create Cluster
In this guide we'll learn how to ingest data from Kafka, a stream processing platform.
Install and Launch Kafka
Let's start by downloading Kafka to our local machine.
To pull down the latest Docker image, run the following command:
docker pull wurstmeister/kafka:latestNext we'll spin up a Kafka broker:
docker run \
--network pinot-demo \
--name=kafka \
-e KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT=zookeeper:2181/kafka \
-e KAFKA_BROKER_ID=0 \
-e KAFKA_ADVERTISED_HOST_NAME=kafka \
wurstmeister/kafka:latestData Source
We're going to generate some JSON messages from the terminal using the following script:
import datetime
import uuid
import random
import json
while True:
ts = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%fZ")
id = str(uuid.uuid4())
count = random.randint(0, 1000)
print(
json.dumps({"ts": ts, "uuid": id, "count": count})
)
datagen.py
If you run this script (python datagen.py), you'll see the following output:
{"ts": 1644586485807, "uuid": "93633f7c01d54453a144", "count": 807}
{"ts": 1644586485836, "uuid": "87ebf97feead4e848a2e", "count": 41}
{"ts": 1644586485866, "uuid": "960d4ffa201a4425bb18", "count": 146}Ingesting Data into Kafka
Let's now pipe that stream of messages into Kafka, by running the following command:
python datagen.py |
docker exec -i kafka /opt/kafka/bin/kafka-console-producer.sh \
--bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--topic events;We can check how many messages have been ingested by running the following command:
docker exec -i kafka kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.GetOffsetShell \
--broker-list localhost:9092 \
--topic eventsOutput
events:0:11940And we can print out the messages themselves by running the following command
docker exec -i kafka /opt/kafka/bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh \
--bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--topic eventsOutput
...
{"ts": 1644586485807, "uuid": "93633f7c01d54453a144", "count": 807}
{"ts": 1644586485836, "uuid": "87ebf97feead4e848a2e", "count": 41}
{"ts": 1644586485866, "uuid": "960d4ffa201a4425bb18", "count": 146}
...Schema
A schema defines what fields are present in the table along with their data types in JSON format.
Create a file called /tmp/pinot/schema-stream.json and add the following content to it.
{
"schemaName": "events",
"dimensionFieldSpecs": [
{
"name": "uuid",
"dataType": "STRING"
}
],
"metricFieldSpecs": [
{
"name": "count",
"dataType": "INT"
}
],
"dateTimeFieldSpecs": [{
"name": "ts",
"dataType": "TIMESTAMP",
"format" : "1:MILLISECONDS:EPOCH",
"granularity": "1:MILLISECONDS"
}]
}Table Config
A table is a logical abstraction that represents a collection of related data. It is composed of columns and rows (known as documents in Pinot). The table config defines the table's properties in JSON format.
Create a file called /tmp/pinot/table-config-stream.json and add the following content to it.
{
"tableName": "events",
"tableType": "REALTIME",
"segmentsConfig": {
"timeColumnName": "ts",
"schemaName": "events",
"replicasPerPartition": "1"
},
"tenants": {},
"tableIndexConfig": {
"loadMode": "MMAP",
"streamConfigs": {
"streamType": "kafka",
"stream.kafka.consumer.type": "lowlevel",
"stream.kafka.topic.name": "events",
"stream.kafka.decoder.class.name": "org.apache.pinot.plugin.stream.kafka.KafkaJSONMessageDecoder",
"stream.kafka.consumer.factory.class.name": "org.apache.pinot.plugin.stream.kafka20.KafkaConsumerFactory",
"stream.kafka.broker.list": "kafka:9092",
"realtime.segment.flush.threshold.rows": "0",
"realtime.segment.flush.threshold.time": "24h",
"realtime.segment.flush.threshold.segment.size": "50M",
"stream.kafka.consumer.prop.auto.offset.reset": "smallest"
}
},
"metadata": {
"customConfigs": {}
}
}Create schema and table
Create the table and schema by running the appropriate command below:
docker run --rm -ti \
--network=pinot-demo \
-v /tmp/pinot:/tmp/pinot \
apachepinot/pinot:1.0.0 AddSchema \
-schemaFile /tmp/pinot/schema-stream.json \
-tableConfigFile /tmp/pinot/table-config-stream.json \
-controllerHost pinot-controller \
-controllerPort 9000 -execQuerying
Navigate to localhost:9000/#/query (opens in a new tab) and click on the events table to run a query that shows the first 10 rows in this table.
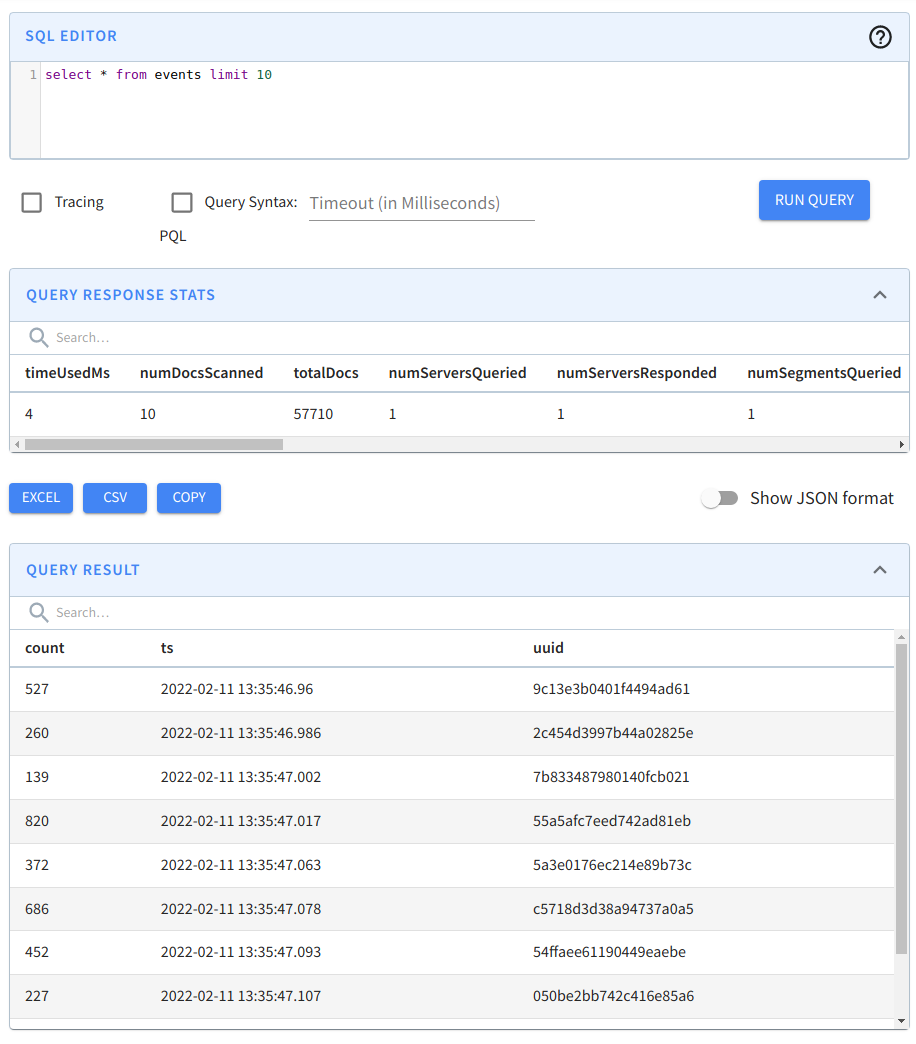 Querying the events table
Querying the events table