Managed Offline Flow
In this guide we'll learn about Managed Offline Flow, which is Apache Pinot's way of transitioning data from real-time to offline tables.
The managed offline flow process is done using the Real-Time to Offline Job. This guide explains how it works, but if you want to get it configured on your Pinot Cluster, see the following guides:
Why do we need this?
Pinot is most commonly used for providing real-time analytics based on streaming data, which can be achieved using a real-time table. However, after running these systems for a while, we'll want to update the data that's been ingested into this table. Perhaps the name of a value in a column has been updated or we want to remove some duplicate records.
Segments in real-time tables can't be replaced, but we can replace those in offline tables. Managed offline flow is the way that Pinot handles the process of moving the data from real-time to offline tables.
How does it work?
There are two parts to the process: task generation and task execution. Let's look at each in turn.
Task Generation
Once the real-time to offline job has been scheduled, the task generator (running on the Pinot Controller) will create tasks to be run by a Pinot Minion (opens in a new tab).
The generator determines the window start and end time based on the provided configuration. It will then check to see if any of the completed segments are eligible by checking their start and end time, starting from the segment with the earliest time. Eligible segments must overlap with that window, as shown in the diagram below:
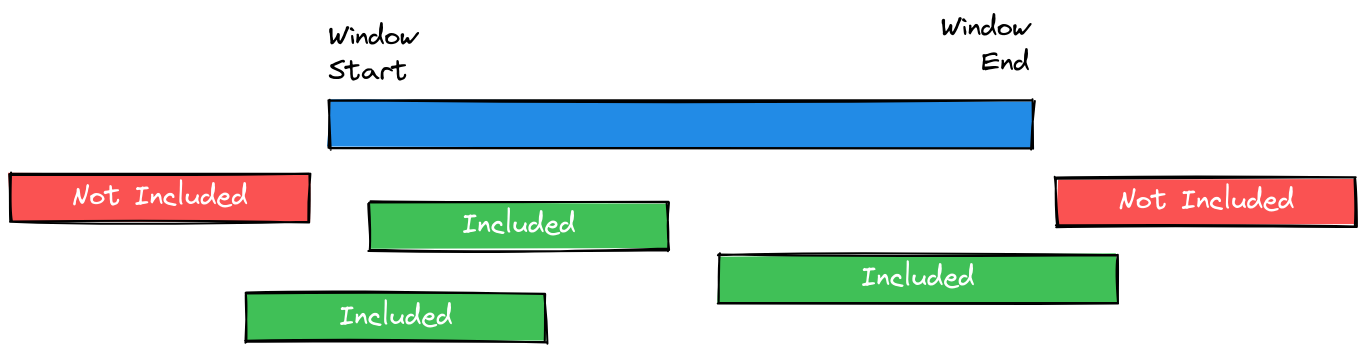 Real-Time to Offline Job - Selecting eligible segments
Real-Time to Offline Job - Selecting eligible segments
There must be at least one completed/flushed segment in the real-time table, otherwise the task won't try to create any offline segments.
As long as some segments match the window, a task will be created and sent to the Minion. If no matching segments are found for the window, the generator will move to the next time window and repeat the process.
When the generator is checking the most recently completed segment, it will make sure that the segment crosses over the end of the window to make sure that the consuming segment doesn't contain some portion of the window.
Task Execution
Once the Minion receives a task to execute, it does the following steps:
- Downloads the existing segments.
- Filter records based on the time window
- Round the time value in the records (optional)
- Partition the records if partitioning is enabled in the table config
- Merge records based on the merge type
- Sort records if sorting is enabled in the table config
- Uploads new segments to the Pinot Controller.
Querying
The data written to segments in offline tables won't immediately be seen in query results. When a query is received by a Pinot Broker, the broker sends a time boundary annotated version of the query to the offline and real-time tables.
- For more on time boundaries, including how they're computed and used by the Pinot Broker, see Concepts: Time Boundary.
- If you want to know how to determine the time boundary for your table, see How to compute time boundaries.
Real-Time table segment retention
This job does not remove any segments from the real-time table.
The RetentionManager is responsible for data retention, which it determines based on the retention time specified in the real-time table config.